What is the
WQ ToolBox?
time-saving software tools for aquaculture
time-saving software tools for aquaculture
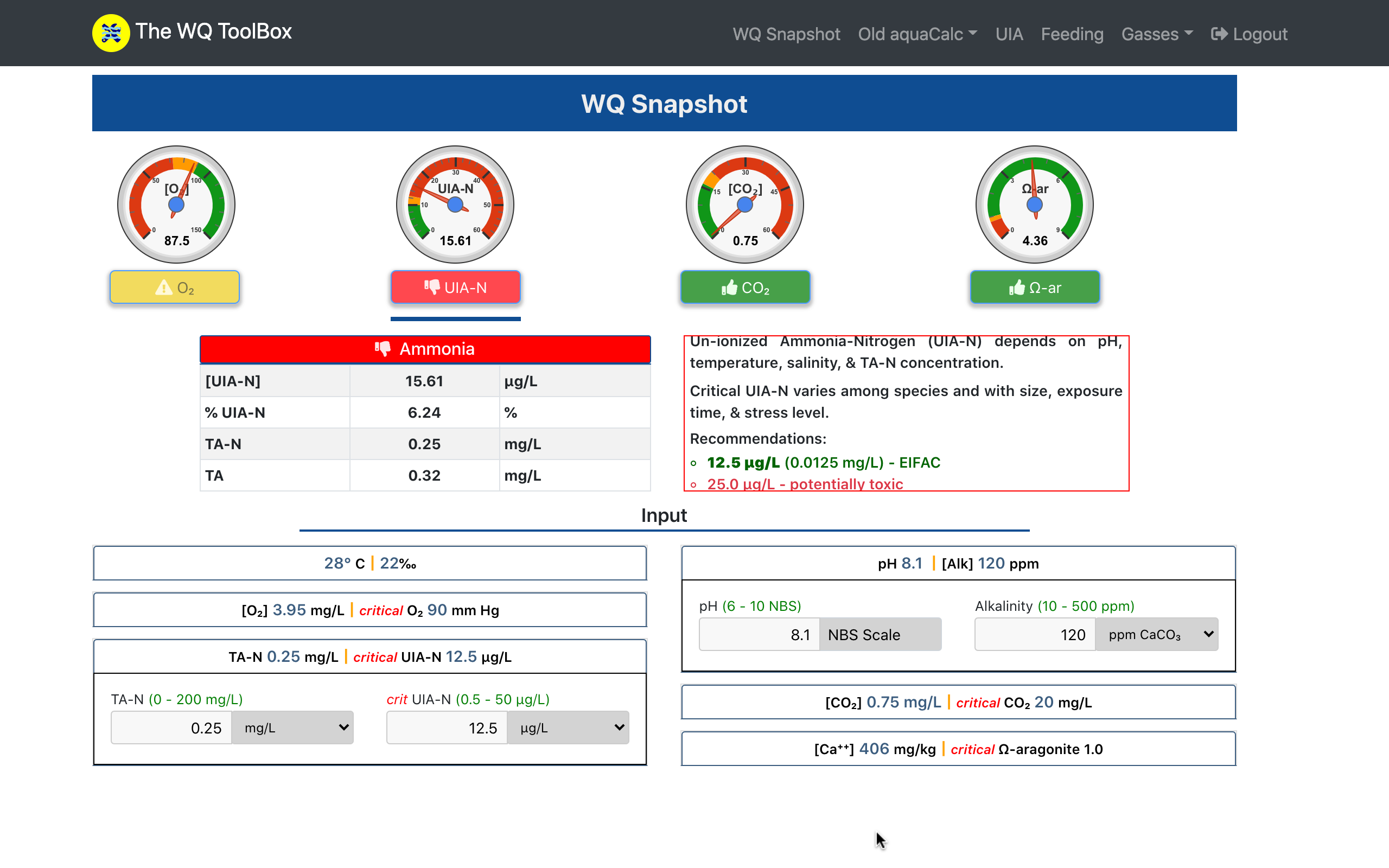
The WQ Snapshot displays four key RAS properties...
A variety of units reduces the need for conversions and visual cues indicate safe, warning, & danger levels.
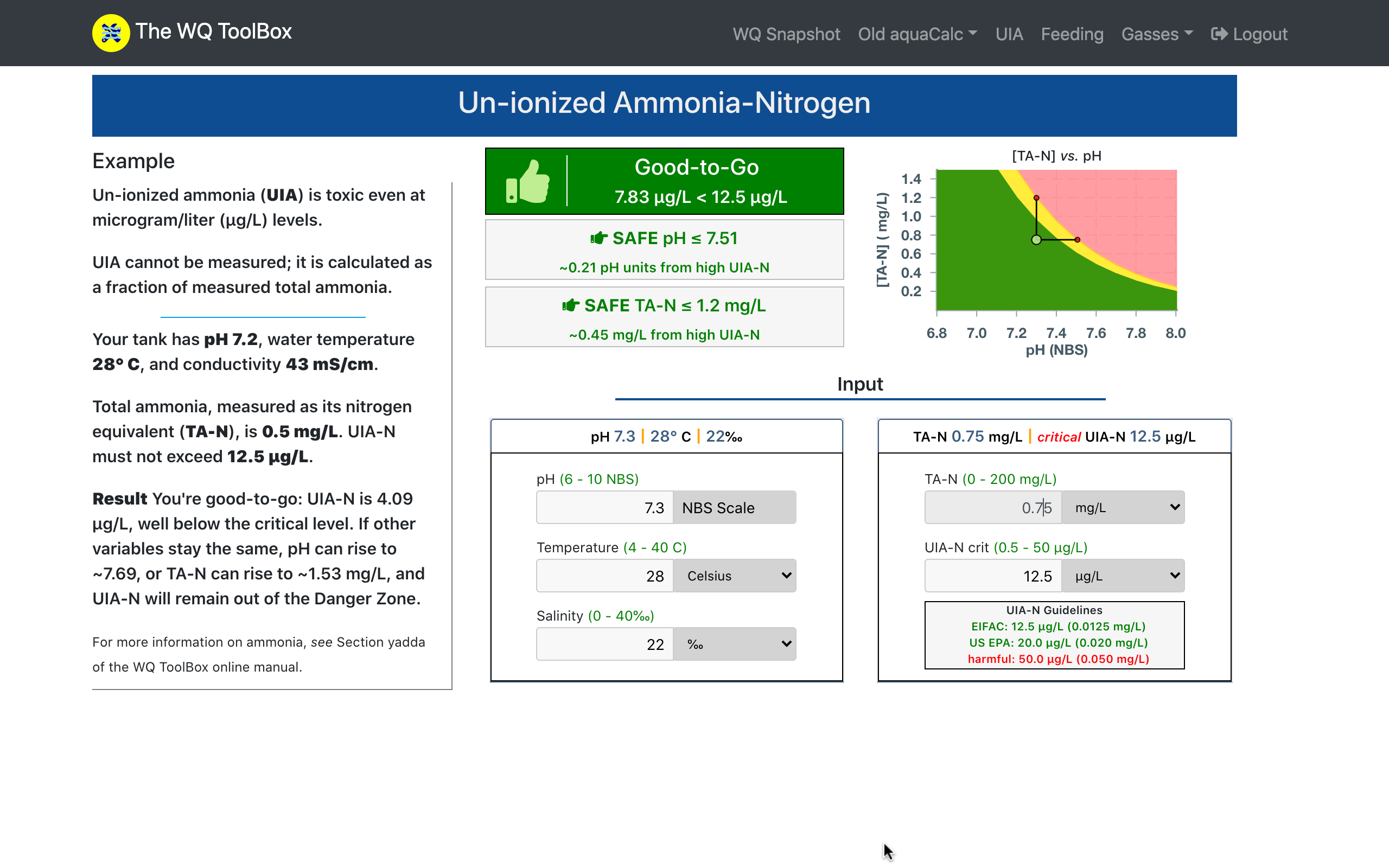
UIA-N is toxic to aquatic animals at microgram/L levels.
This WQ ToolBox tool's Cæsar's Thumb clearly tells you if your water is good-to-go () or not () according to your species's critical UIA-N threshold.
But that's not enough for precision RAS management.
The tool is enhanced to quantify & plot your culture water's state relative to the UIA-N Danger Zone.

Unit conversions are a time-consumng pain that slows the routine aquaculture work-flow.
The WQ ToolBox performs common (length-area-volume) and aquaculture-releated conversions quickly & accurately in both metric & English units.
Biomass & abundance are converted between per-unit-area and -volume. Composite quantities (e.g. Hydraulic Load Rate & Flow Rate) may be calculated & converted in a single operation.

Unit conversions of dissolved gasses can prove confusing.
Part of the confusion comes from converting between units of concentration and units of pressure (tension).
Pressure units are preferred: It is the pressure gradient, not the concentration gradient, that drives respiration.
Additionally, because some aquaculturists do not measure dissolved CO₂, this tool optionally will estimate it from pH, alkalinity, temperature, & salinity.

The need to mix water types arises when preparing the culture environment & when adding water lost from evaporation.
Mixing temperature, salinity, alkalinity, & TA-N is simple: Multiply the property by the water type's fractional contribution to the final volume, then add all terms.
pH is more complicated because buffering affects the final level of pH-dependent properties, such as UIA-N.
The WQ ToolBox handles that complication (and more) to perform this aquaculture task quickly & accurately.
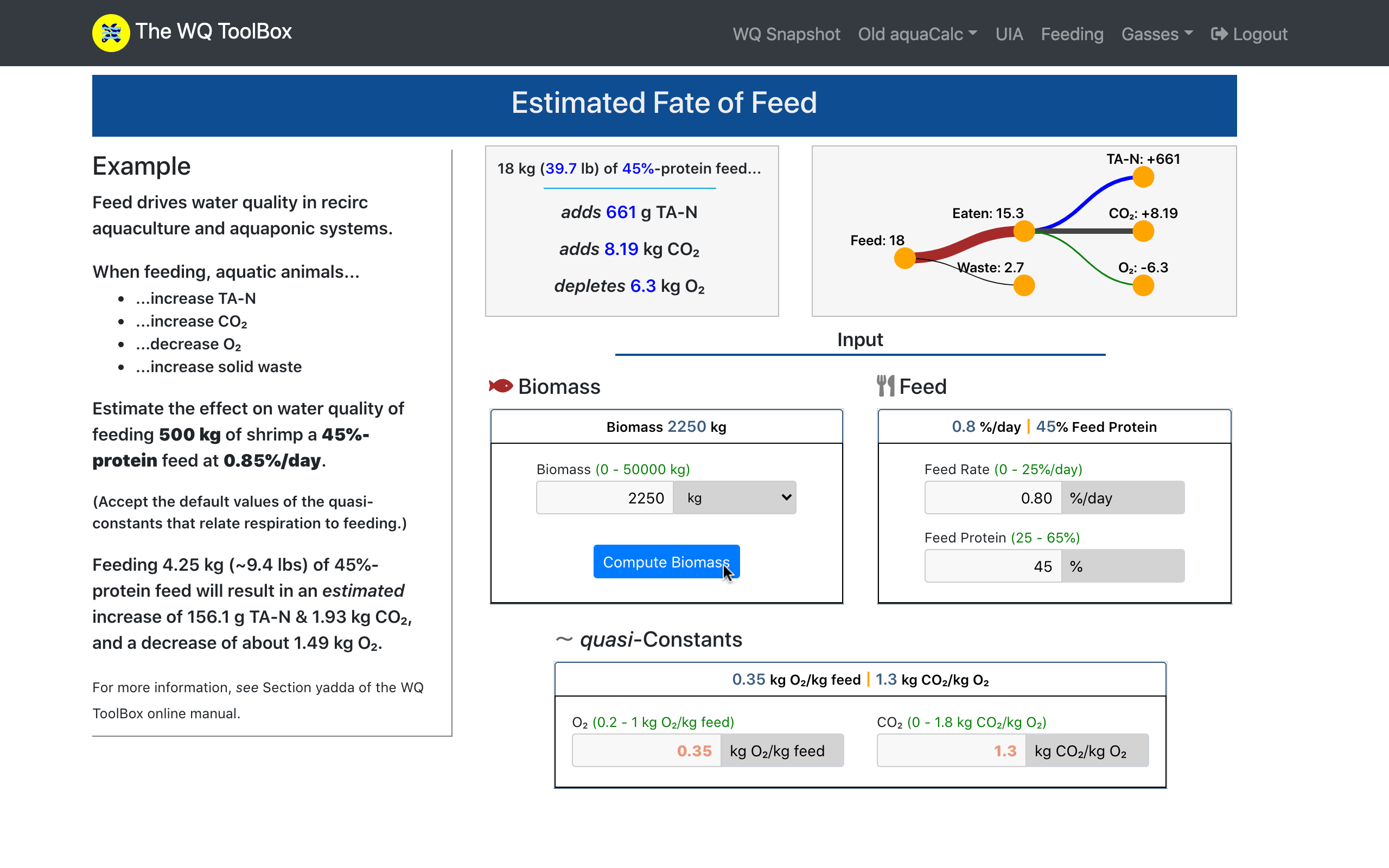
Feed fuels growth -- but it also degrades water quality.
When aquatic animals feed, they...
This WQ ToolBox tool helps users anticipate the effects of feeding on water quality. (It also is used by the WQ Map to plot the feed-effect vector.)

TGP is the sum of the partial pressures of all dissolved gasses, mainly N₂ & O₂, but also CO₂, argon, & water vapor.
When TGP exceeds barometric + hydrostatic pressure, culture water is super-saturated. That exposes stock to Gas Bubble Disease (GBD) — the ‘bends’ of divers.
GBD reduces stock health and, when excessive or prolonged, can be fatal.
This tool carries out the many calculations & conversions to solve TGP problems quickly & accurately.
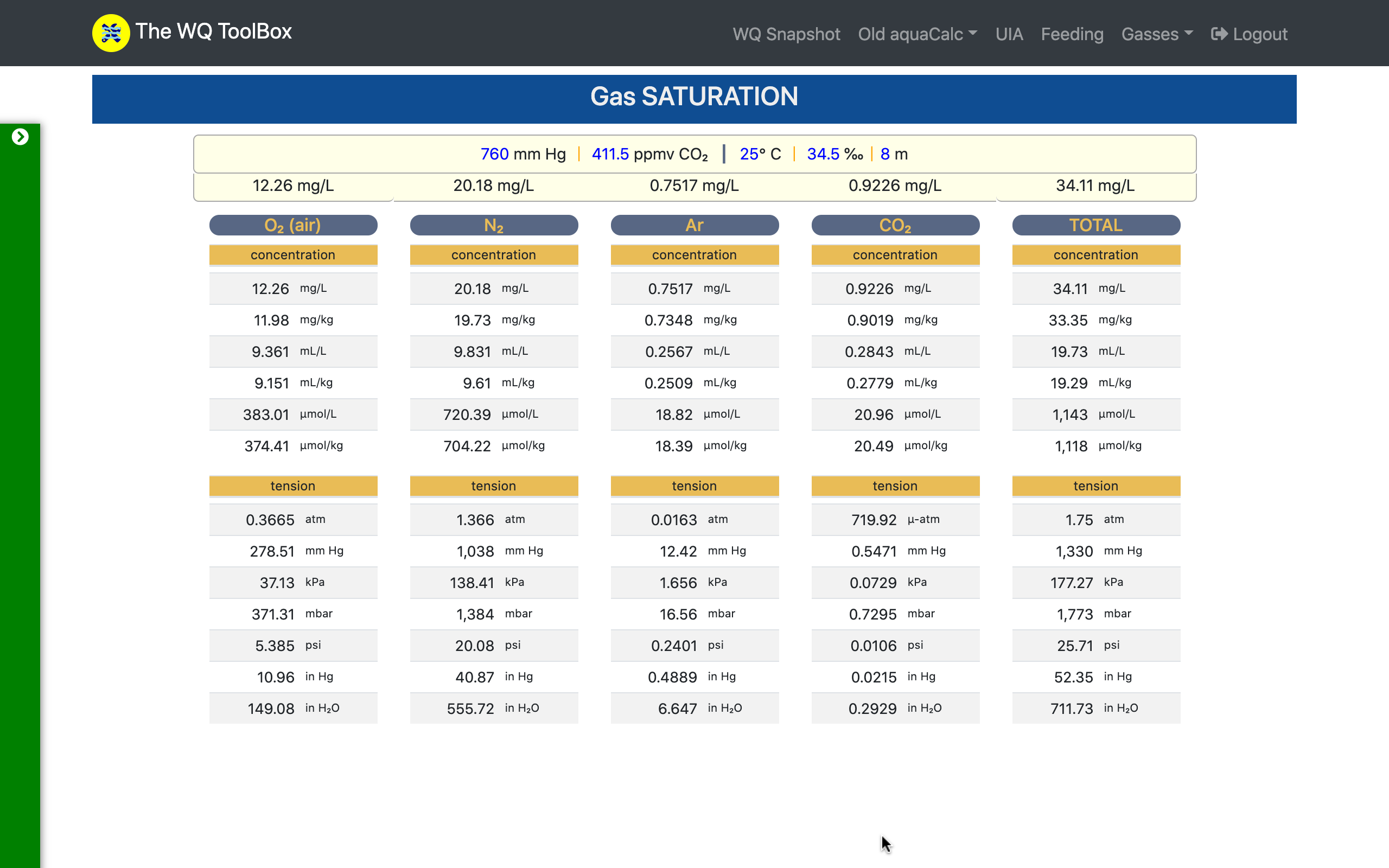
Gas saturation calculations play a role in system design, equipment selection, & production ops.
This tool simplifies your work-flow by cutting through the cumbersome calculations to produce clear results in six concentration units & seven pressure units.
Barometric pressure can be entered directly in common atmospheric pressure units or estimated from altitude.
Water depth may be input when sub-surface gas saturation is a design criterion.

Users sometimes design their own DIY tanks for production or for a variety of ad hoc purposes.
The WQ ToolBox tank design tool speeds up that process by calculating dimensions, bottom-cone angles, & volumes for tanks with circular, rectangular, & oval geometries.
It also profiles water volume & mass vs. fill-depth.
As with other tools, results may be expressed in a variety of common metric & English units without burdening the user with performing explicit conversions.

The amount of time remaining in a LOX dewar (a specialized LOX tank) is critically important when transporting stock to a production facility or live-hauling to market.
The WQ ToolBox uses LOX volume, flow rate, & estimated dewar leakage to perform that calculation.
Flow rate may be entered directly or computed using hauling-tank volume and Wurts's recommendation.
The result is displayed concisely at the top.

Extending RAS production to seasonal climates requires heating culture water to insure good growth.
This WQ ToolBox tool takes the confusion out of selecting a water heater and juggling kilowatts, kilowatt-hours, BTUs, & BTUs/min. It estimates...
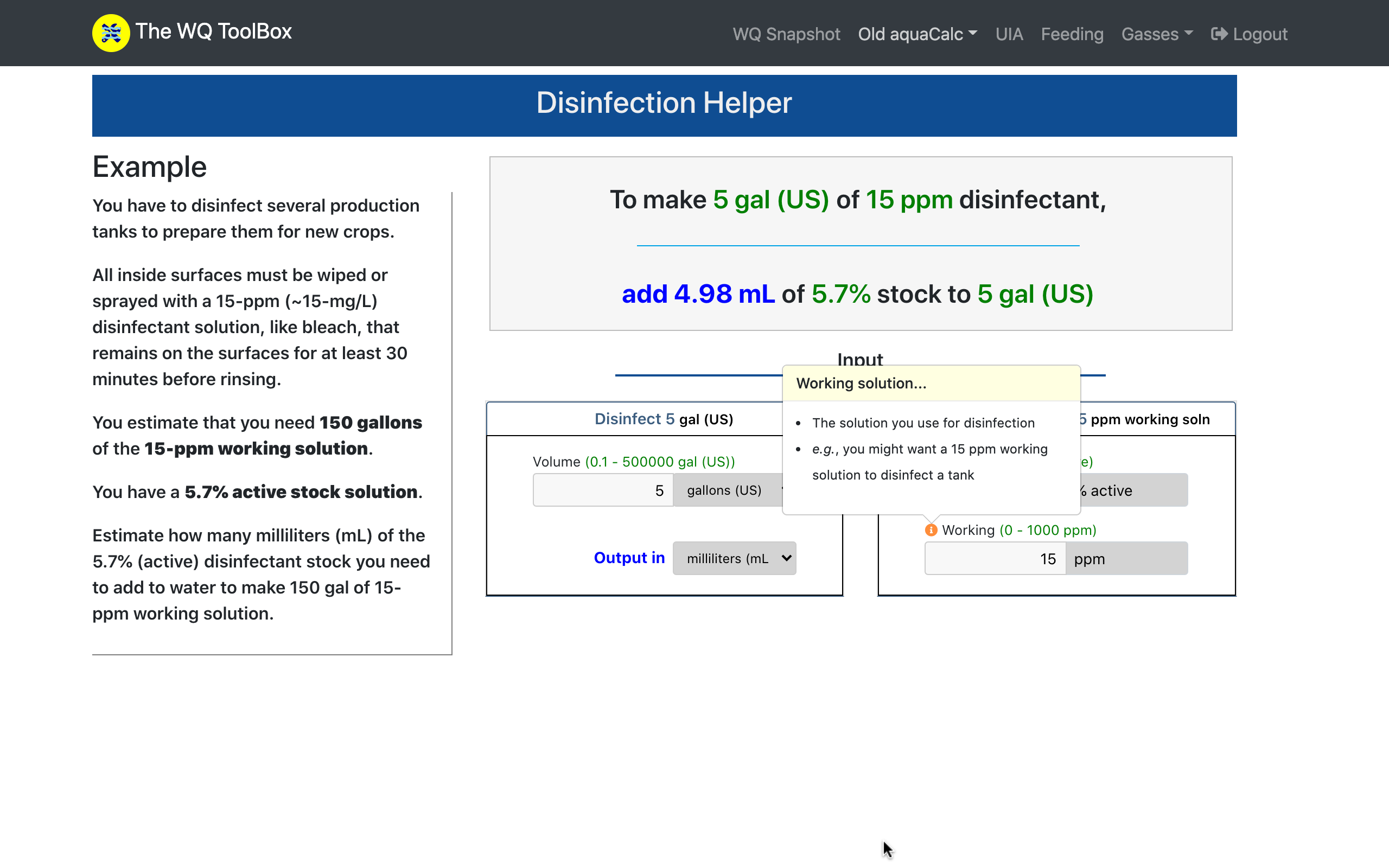
Disinfection is a routine task in every production facility to reduce the chance of a crop-damaging disease.
It's essential to use the correct disinfectant concentrations, and the calculation is simple enough.
This WQ ToolBox tool double-checks that you've prepared the correct concentration of the working solution from the stock solution for the job at-hand.