What is the
WQ Manual?
an interactive resource for WQ training
an interactive resource for WQ training
The WQ Map & the WQ ToolBox provide users with the competence to control aquaculture water quality.
This means that the software can be used without understanding the principles of natural water chemistry.
The companion WQ Manual builds comprehension by diving into important water-chemistry principles at the core of the software.
But why bother to learn tech principles if the software is all I need to manage my water chemistry?

Short answer: You don't have to swim in the deep end of chemistry & math to control WQ; just use the software.
(Similarly, you don't have to comprehend the physics of the internal combustion engine to be competent to drive a car.)
But if you do take the plunge, you'll be able to...
In short, competence + comprehension will make you a more complete & confident WQ manager.

Essential concepts at the foundation of aquaculture WQ -- e.g., alkalinity, pH scales, chemical activity, ammonia-N vs. ammonia... -- often are poorly understood or even ignored.
That limits how far a user can advance their understanding of aquaculture WQ management.
The WQ Manual addresses this in several ways.
For example, it reduces the confusion of scientific jargon by presenting vocabulary & key take-aways with plain-language explanations.

Chemical & math equations typically are high hurdles to overcome in aquaculture WQ discussions for all but specialists.
Some sources opt for no (or very few) equations. That places a strict limit on how well important WQ topics can be developed.
Standard WQ texts are replete with equations on every page, but that approach limits their audience to academics.
The WQ Manual strikes a balance: Key equations are explained in a step-by-step manner and, when needed, interactive playgrounds are used to enhance understanding.

The WQ Manual supplements explanations of aquaculture water chemistry concepts with interactive playgrounds.
Interactivity is more effective than traditional media alone -- text, tables, static graphs, & equations. It engages users in a way that brings complicated tech concepts to life.
The example illustrated here clarifies the non-linear nature of pH: Small pH changes represent large changes in acidity. Users change pH values and see surprisingly large increases (or decreases) in culture-water acidity. This contributes to cementing the need for precise WQ management.

The Water Quality Whack-a-Mole game is another interactive playground in the WQ Manual.
The goal is to help users understand a non-trivial aspect of managing pH that's much more difficult to motivate with words & equations alone.
As users change pH & TA-N, they get clear visual feedback on whether or not their chosen pH is optimal.
This builds an intuitive understanding of a key WQ management problem that is at the core of the WQ Map.

WQ playgrounds also are useful for clearing up a few common misconceptions about aquaculture water chemistry.
For example: neutral pH is not always 7.0; changing CO2 does not affect alkalinity; and adding only bicarbonate almost never is sufficient for managing water quality.
The interactive playground pictured here lets users change temperature & salinity to visualize how neutral pH depends on both and can vary significantly from 7.
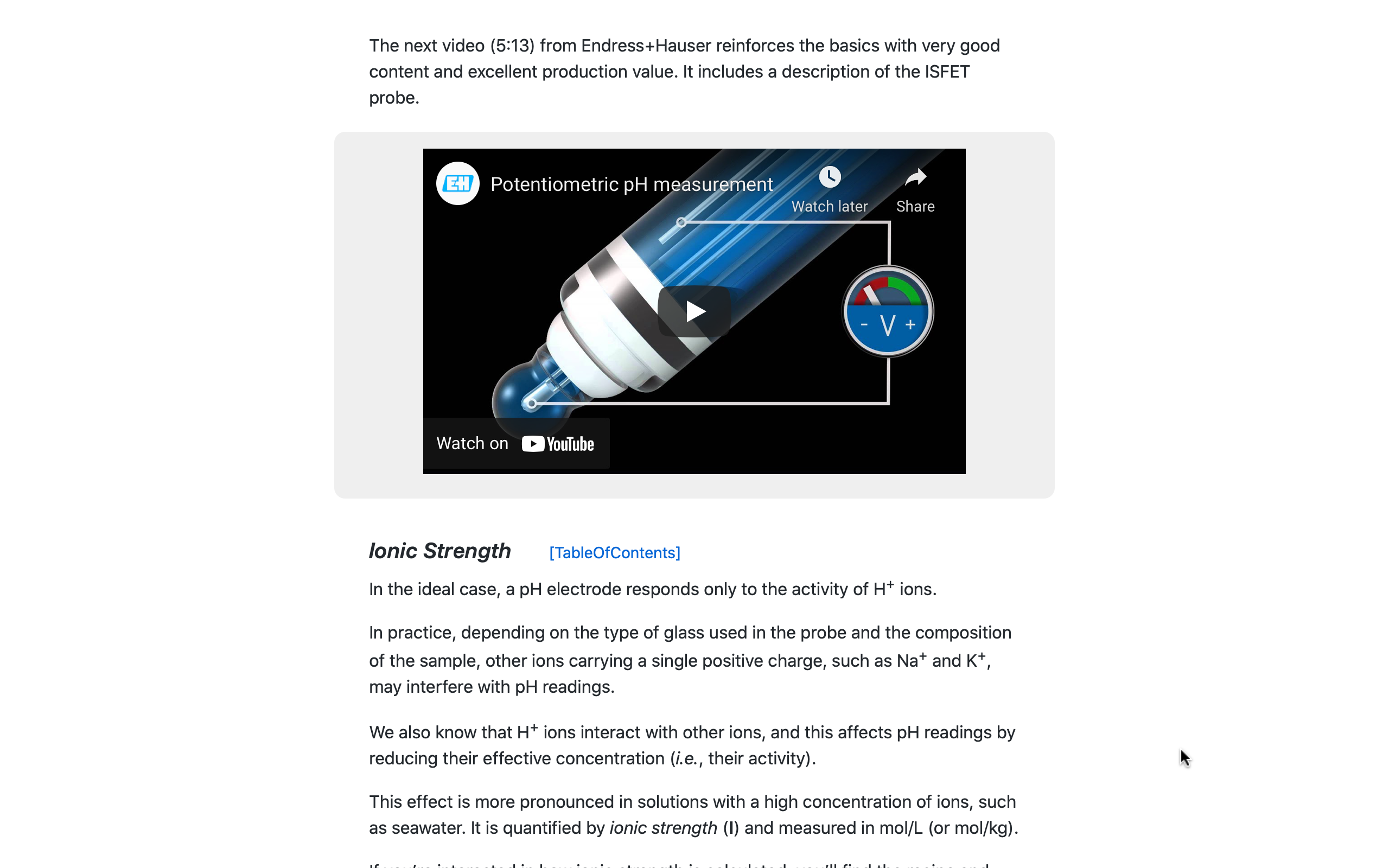
Several third-party videos are included in the WQ Manual to enhance certain content.
This is the tactic of 'effective redundancy': After presenting a topic, repeating the same material in a different "voice" and with a different presentation style reinforces concepts that become more familiar with each repetition.
Pictured here, an explanatory video on the standard glass electrode used for pH measurements, along with an introduction to the solid-state ISFET pH sensor.

Optional material -- technical & historical -- is available throughout the WQ Manual in expandable panels.
Tech topics delve deeper into, for example, the difference between concentration & activity; moles as a fundamental unit of concentration; the seawater pH scales; and how to calculate ionic strength.
Where possible (as in the accompanying popcorn images), familiar analogies help wring some of the "tech" out of otherwise confusing water chemistry topics.
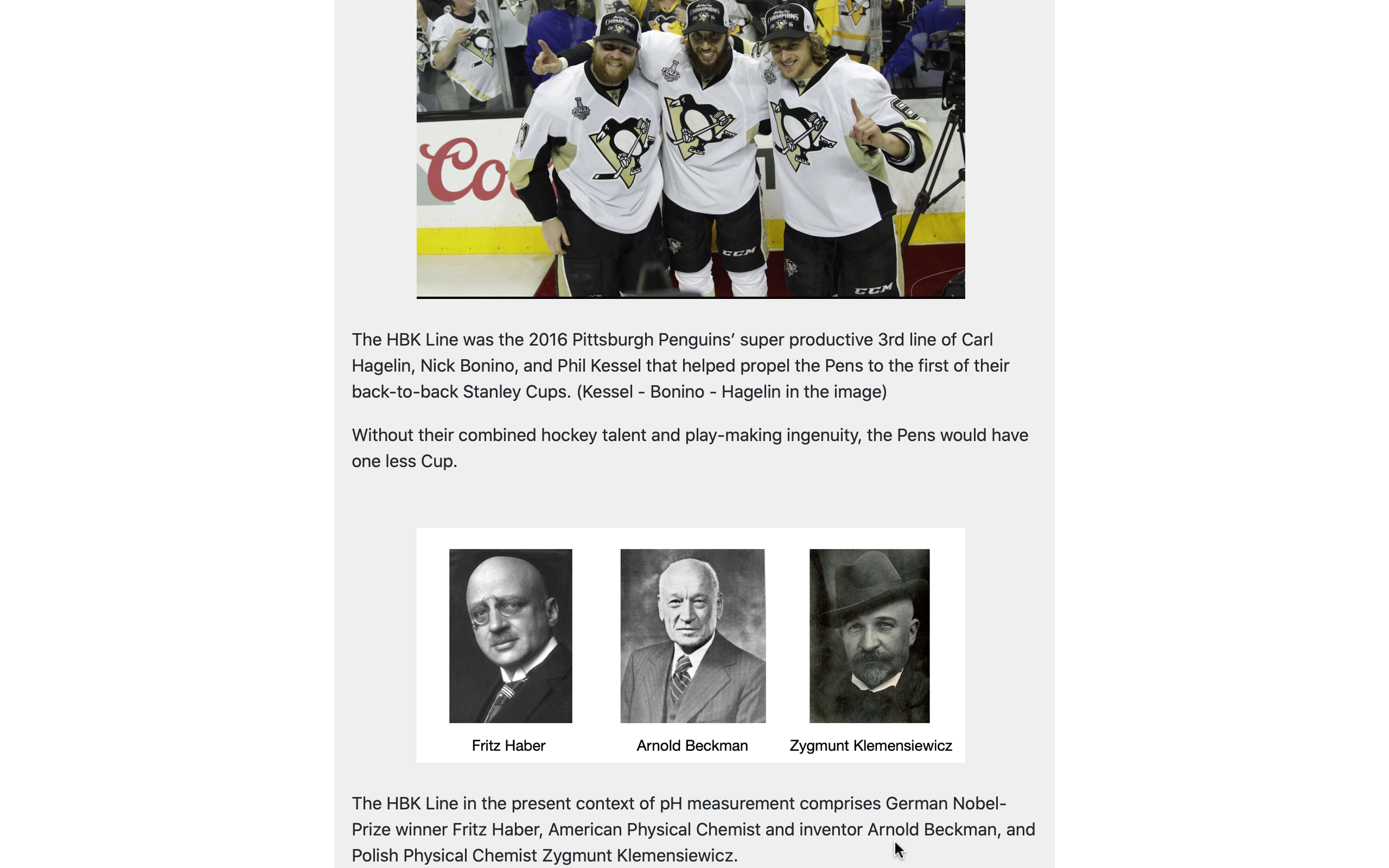
Other optional panels present users with some brief historical background on topics related to natural water chemistry.
These include: the meaning of the p in pH (a small, but interesting, matter); the origins of the ubiquitous pH electrode; and why base-10 logarithms are used to define pH.
Such side-issues are not directly related to the practice of aquaculture water-quality management, but they satisfy the curiosity of many users and add a bit of depth to their general knowledge of water chemistry.